IoT supply chain management has long been touted as the solution for better logistics management and tracking. Companies have followed the trend, with a recent PwC survey suggesting that the Internet of Things is the second most popular technology adopted across the supply chain.
Yet, as the same research shows, most investments haven’t fully delivered. The reasons fall into two main buckets: organizational (e.g., a company fails to articulate a clear vision or manage change) and technical (they simply lack the skills or technology to deal with logistics software development and implementation).
This article looks at the technical side and best practices of effective IoT adoption. In it, I’d like to explain the relationship between IoT and supply chain efficiency based on real-life use cases. Here you can also find out several ways to tackle challenges such as connectivity, cybersecurity, interoperability, and data quality.
The Role of IoT in Supply Chain Management & Logistics
Supply chain professionals use IoT to build and monitor a network of interconnected systems. A network comprises different elements:
- Sensors on assets and equipment that collect data such as location, vehicle health, or temperature conditions
- Transmission networks that connect these devices to ensure data sharing across the supply chain
- Analytics software tools that transform the data into actionable insights for route optimization, predictive maintenance, and more
The potential of such networks to optimize supply chain operations is huge and drives a healthy investment outlook. Industry research from Markets and Markets predicts that the value of the global IoT market will almost double over five years, rising from $18.95 billion in 2022 to $34.81 billion by 2027.

More specifically, IoT transforms supply chain and logistics processes in three main areas:
- Monitoring: You can monitor the movement, distribution, and condition of assets such as vehicles, equipment, and inventory.
- Real-time updates and scheduling: IoT systems can also automatically update inventory levels, process orders, and schedule deliveries.
- Proactive incident reduction: Real-time IoT connectivity helps head off problems before they happen. For example, you can change a delivery route to avoid likely disruptions or schedule vehicle maintenance before a breakdown occurs.
Let’s dive deeper into how IoT improves your operational efficiency.
Benefits of the Internet of Things in Supply Chain Management
Data analytics and monitoring devices have revolutionized supply chain management. Here’s a breakdown of the main applications of IoT in supply chain management and logistics, with real-world examples.
Optimized logistics efficiency and planning
IoT sensors such as GPS modules and RFID tags provide asset tracking in real-time, meaning you can monitor your product 24/7 on its journey from warehouse to retail shelves. This, in turn, helps you optimize routes and give accurate delivery times to customers.
Techstack Case
Managing a large IoT network requires an algorithm that processes information from multiple data points. These include sensor readings, device status, metadata, and other physical parameters. Techstack developed such an algorithm to streamline the cargo auction system for a client in the transportation industry.
Read full caseAn IoT system can also help you take corrective action faster. For example, if a shipment is delayed, the IoT system can alert the logistics manager, who can then notify the customer or rearrange schedules.
Inventory and resource management
You can also use IoT for inventory control. Tracking devices and smart tags can help optimize stock levels in warehouses—for example, weight sensors on shelves can detect when stock is running low and trigger a replenishment order.
Amazon, naturally, relies heavily on IoT for warehouse operations. The company integrates sensors and autonomous robots that perform mundane tasks, like sorting blue GoCarts. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries has also implemented IoT and AI for driverless forklifts.
IoT for inventory requires regular audits to validate system accuracy. This makes centralized storage and analytics software key to keeping inventory data reliable.
Reduced downtime with predictive maintenance
IoT sensors can help detect early signs of wear in equipment, predicting failures before they occur. Real-time data is transmitted to analytical ML-based software. ML model, trained on historical maintenance data, helps forecast equipment strain based on various factors.
As an example, sensors on a conveyor belt in a distribution center can predict when a part will fail. By automatically alerting maintenance teams, you can prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend equipment lifetime.
Deloitte’s 2022 Predictive Maintenance report quantifies the gains. Among other things, IoT-enhanced technology reduces equipment repair costs by 3-5% and facility downtime by 5-15%. It also increases labor productivity by up to 20%.
Predictive maintenance has become a particularly high-return investment for industrial businesses. Research shows that the market for predictive maintenance solutions will grow from $5.5 billion in 2022 to $28.2 billion in 2026.
Cold chain monitoring
IoT sensors are crucial for cold chain monitoring. Sensors can detect changes in storage conditions (like temperature or moisture meters) in a truck or warehouse containing perishable goods. Data is sent to a central system or cloud application which monitors temperatures. Any deviations from the required temperature range trigger immediate alerts.
The cold chain tracking market is projected to reach $19.4 billion by 2030 (up from $6.1 billion in 2022), based on 2023 data. IoT for temperature monitoring is particularly widespread in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
Resilient supply chain distribution
The fluctuations in customer demand, traffic, and weather conditions also call for smarter decision-making and planning. As McKinsey reports, IoT and data analytics with machine learning capabilities are used for demand forecasting models and business planning.
Analyzing trends and patterns lets you identify potential supply vulnerabilities and develop contingency plans. For example, traffic and weather sensors can flag potential delays, allowing you to reroute shipments proactively. You can also use real-time IoT data to react faster to unexpected events, such as a sudden spike in demand or a supply chain disruption.
McKinsey found that even early adopters of IoT have seen improvements in supply chain management. They also suggest that IoT implementation could reduce logistics costs by 15%, improve inventory levels by 35%, and boost service levels by 65% (compared to non-IoT competitors).
Improved customer experience
IoT empowers logistics companies to offer a more personalized customer experience and timely deliveries. With IoT, you can tailor services to individual customers by analyzing previous data and delivery histories—for example, by optimizing delivery times for customers based on previous orders.
With IoT-tracked shipments, you can also give customers up-to-date information on their orders. This transparency helps build trust and improves customer satisfaction.
Maximized cost savings
All the applications above lead to attractive cost savings. For example:
- Proactive maintenance lets you avoid costly repairs and downtime. Deloitte suggests that predictive maintenance has helped companies become more profitable, citing the example of a US energy and oil company, which reduces operational expenses by eliminating breakdowns.
- Real-time inventory management minimizes the costs associated with overstocking and stock shortages.
- Data on fuel consumption, vehicle speeds, and even driving patterns lets you pinpoint bad driving habits (like speeding) and optimize routes.
To sum up, successful IoT implementation can improve processes throughout the supply chain, resulting in higher productivity and reduced costs.
Technical Challenges of IoT Integration for Supply Chain Management
IoT paints a bright future for supply chain and logistics, but effective implementation is a challenge. A meager 17% of executives interviewed for PwC say their investments have fully paid off, citing problems with connectivity, security, data quality, interoperability, and a lack of talent.
Let’s see what you can do to avoid the same pitfalls.
Unreliable data connectivity
Connectivity is crucial for real-time logistics data. IoT applications require stable connections to monitor devices accurately and respond to disruption.
Edge computing offers one solution to connectivity challenges. Edge devices collect data, while complex calculations occur in the cloud. This helps accelerate data transfer between your sensors and the central network. It also reduces the processing burden on central servers, freeing up your resources.
Investment in 5G network infrastructure is another option. 5G technology has the potential to enhance connectivity and reduce latency.
Security vulnerabilities
IBM’s 2022 Cost of a Data Breach Report highlights that critical infrastructure organizations (including the transportation, industrial, and technology sectors) suffer higher costs from data breaches. An average breach for these businesses costs $4.82 million — $1 million more than for other businesses.
The same report suggests that IoT devices could amplify the risks. The average data breach cost is increased by about $150,000 in organizations with an IoT-enabled network.
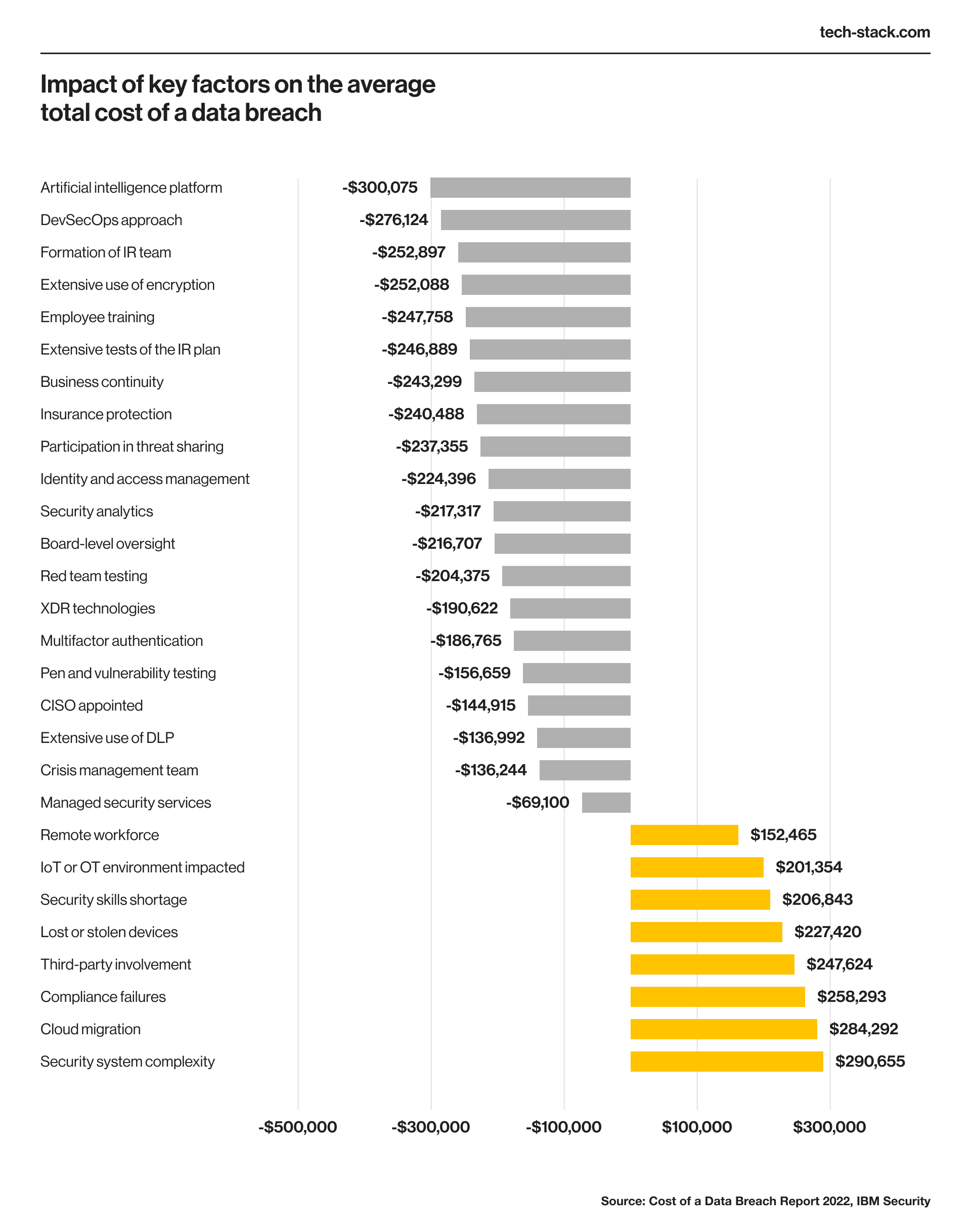
There are four ways you can address this risk:
- Encryption: IoT sensors in the supply chain that communicate through encrypted channels make the transmitted data unreadable to unauthorized third parties.
- Authentication and access control: Role-based data control ensures that employees can only access the data they need for their jobs.
- Anonymization: IoT devices can transmit data related to your customers and employees, so it's crucial to anonymize as much of this data as possible.
- Timely updates: Given the evolving attack vectors, organizations should update their security protocols regularly.
Data quality
As IoT devices and analytics multiply, so does your data overhead. IoT data is usually scattered across internal and cloud repositories, often resulting in data corruption, inconsistencies, and gaps.
One solution is to implement centralized cloud storage. Edge computing can also process data nearer its source, sending only the most relevant data to the cloud. This helps filter out low-quality data and reduces network latency.
You can also use automated anomaly detection and validation to improve data accuracy. This involves developing a pipeline for automating quality control according to pre-defined metrics such as accuracy, completeness, readability, and redundancy. Adding a human expert for oversight can improve the process.
Beyond these techniques, a comprehensive data management strategy is essential for addressing data quality issues. This includes regular data audits to identify and correct errors, inconsistencies, and gaps. Data governance and ownership policies are also vital.
Interoperability issues
One of the main barriers to effective IoT integration is a lack of common standards and protocols for IoT communication. This can easily create a fragmented ecosystem with poor data exchange. Many organizations also have outdated legacy machines and software that require retrofitting before IoT can be practically implemented.
You can overcome this by opting for a cloud platform with open standards. To create a unified network, you might have to rework your communication protocols, data formats, and security policies.
Supply chain vendor Blue Yonder has bitten the bullet by rearchitecting its supply chain suite for a multi-tenant architecture data cloud platform to ensure interoperability. US Customs and Border Protection is also developing interoperability standards. Both initiatives have taken heavy investment, but will pay off by supporting seamless communication in the future.
Other solutions to interoperability issues include adding IoT sensors and gateways to legacy devices and using middleware to translate between protocols.
Lack of expertise
Lack of expertise remains a huge challenge for IoT supply chain management. According to PwC, 2% of executives consider digital native skills essential for successful transformation. Currently, 83% of technology investments don’t deliver the expected results.
Partnering with a specialized logistics or tech company can help you bridge the gap. The right vendor can give you immediate access to expert knowledge and intelligent logistics systems. What’s more, collaboration can empower you with best practices for device deployment, analytics, and data security. Finally, regular workshops, seminars, and continuing education programs can ensure employees are using tools productively.
At Techstack, we specialize in IoT engineering. We develop, test, and integrate software with AI and machine learning capabilities that can enable monitoring of your entire supply chain while ensuring stable connectivity and robust security.
IoT-Enabled Supply Chain Visibility with Techstack
For the supply chain, the Internet of Things is nothing less than a game-changer. When combined with AI-enhanced analytics software, IoT provides exceptional visibility into your operations. It can automate tasks, slash operating expenses, and boost customer satisfaction.
These benefits are substantial, but achieving them takes time and investment. Successful IoT implementation means processing vast amounts of data, improving cybersecurity, and ensuring stable connectivity. You may also have to retrofit your legacy software and equipment.
At Techstack, we’ll help you meet the challenges head-on. Our software development company has completed multiple IoT-based projects, including solutions for manufacturing and transportation. Get in touch to learn more about our services and how we can help you reach your goals.






